9 Foods You Can Eat To Improve Your Skin Texture
By: Priyanka Maheshwari Wed, 24 July 2024 5:10:19
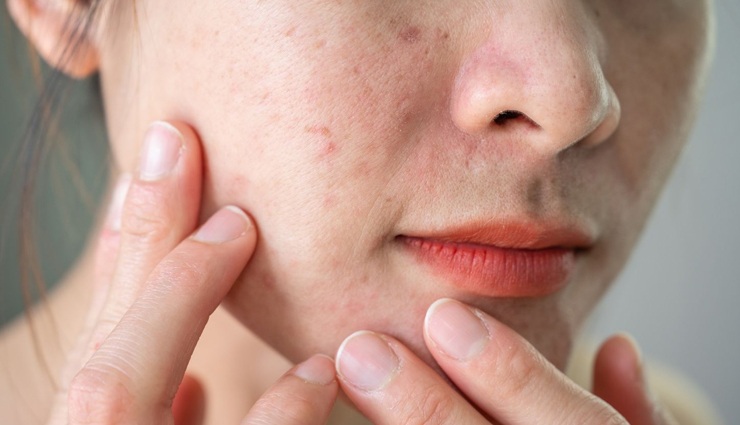
Skin texture refers to the surface quality of your skin, including its smoothness, softness, and overall appearance. It encompasses various characteristics, such as:
* Smoothness - Skin texture can be smooth or uneven. Smooth skin has an even surface, while uneven texture might include bumps, rough patches, or flakiness.
* Clarity - Clear skin typically has a uniform texture without visible blemishes, scars, or discoloration.
* Firmness - Firm skin feels resilient and supple. Loss of firmness can lead to sagging or wrinkles.
* Hydration - Well-hydrated skin is plump and soft, while dry skin may feel rough or tight.
* Elasticity - Healthy skin has good elasticity, meaning it can stretch and bounce back without losing its shape. Reduced elasticity can lead to sagging and wrinkles.
* Pores - The size and appearance of pores can impact skin texture. Enlarged pores may be more noticeable and affect the overall smoothness of the skin.
Improving skin texture often involves a combination of skincare practices, such as regular exfoliation, moisturizing, and using products that address specific concerns like acne, sun damage, or aging. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants can also play a significant role in maintaining healthy skin texture.
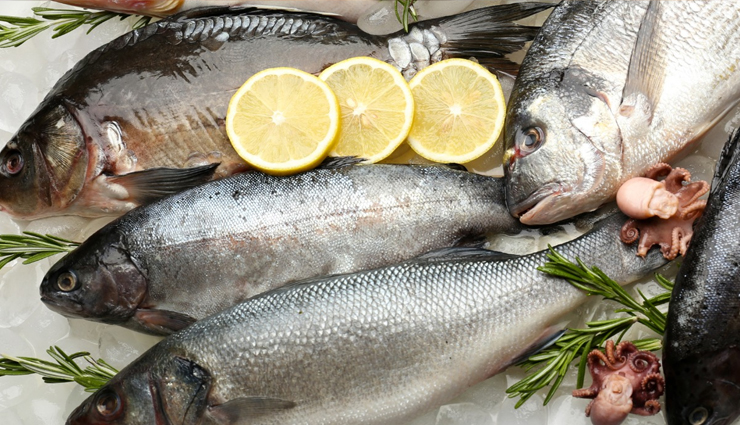

# Fatty Fish
While some individuals with skin concerns avoid fatty foods, it’s important to recognize that not all fats are equal. Cold-water fatty fish like herring, sardines, and salmon are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can be beneficial for the skin. Research from 2016 provides substantial evidence that omega-3 fatty acids may lower the risk of non-melanoma skin cancers, particularly for those at higher risk. These acids can reduce damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation, inflammation, and immunosuppression in the skin. Therefore, a diet high in omega-3 fatty acids may help mitigate inflammatory symptoms and improve skin's resilience against UV rays.
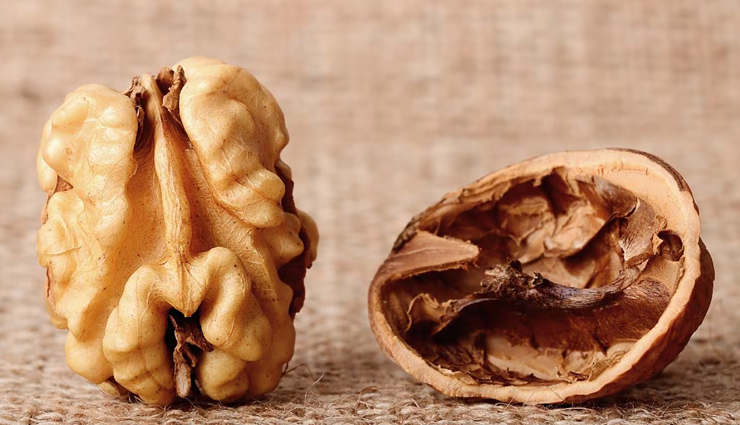

# Walnuts
Nuts can offer similar advantages as fatty fish and are an excellent dietary option, especially for vegans and vegetarians. Walnuts are particularly rich in both omega-3 and omega-6 unsaturated fatty acids. A 2012 review highlighted that many people consume less omega-3 fatty acids than needed for optimal health. Balancing these fatty acids is crucial since a typical Western diet often has excessive omega-6 fats, which can increase inflammation and exacerbate inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
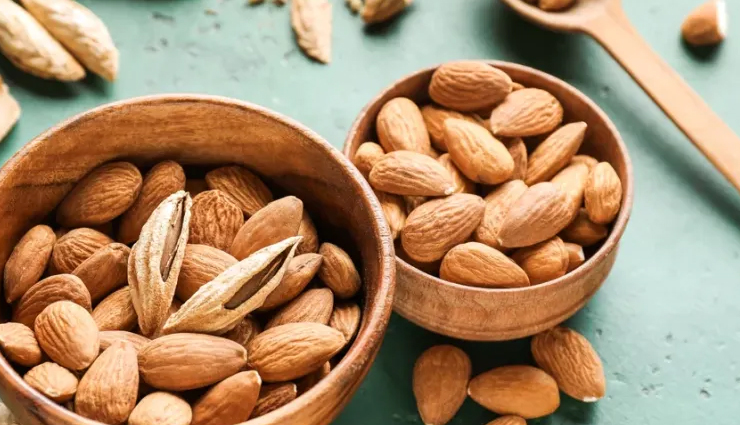

# Almonds
Almonds are a great source of unsaturated fatty acids and are especially rich in vitamin E. Many seeds, including almonds, provide antioxidants and unsaturated fatty acids that can promote healthy skin.
# Sunflower Seeds
Sunflower seeds are another good source of protective fatty oils. They also contain significant amounts of zinc and vitamin E, both of which are beneficial for protecting skin cells, according to data from the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
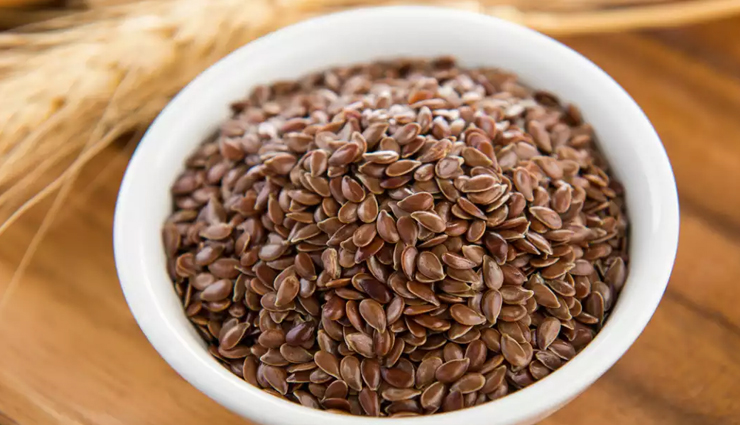

# Flax Seeds
Flax seeds are high in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid. Adding freshly ground flaxseeds to smoothies or salads can boost your intake of omega-3 fats and support skin health. A 2011 study found that women with sensitive skin who took flaxseed oil supplements for 12 weeks experienced reduced sensitivity, roughness, scaling, and improved hydration and smoothness of the skin.
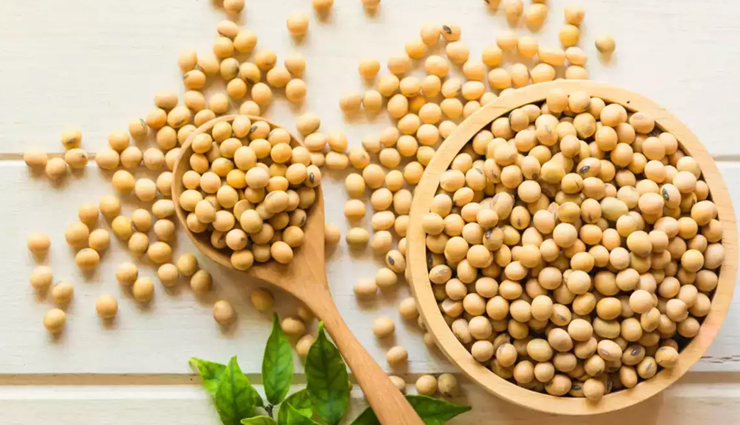

# Soy
Soybeans contain isoflavones, which may be particularly beneficial for skin health, especially in women. A 2017 review found that middle-aged women consuming more soy isoflavones experienced fewer fine wrinkles and better skin elasticity. These isoflavones may be especially effective during menopause, when decreased estrogen levels can affect skin elasticity.
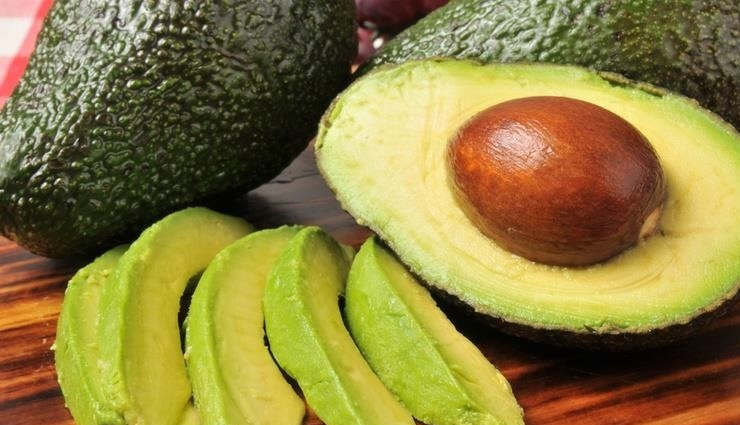

# Avocados
Avocados are rich in healthy fats and vitamin E, both of which support skin health. These essential fats are necessary because the body cannot produce them. A 2013 review noted that avocados also contain compounds like lutein and zeaxanthin, which help protect the skin from UV and visible radiation damage.
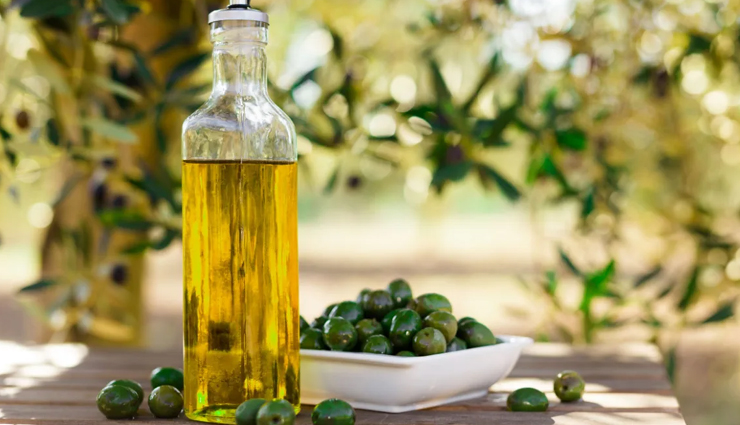

# Olive Oil
Among cooking oils, olive oil is one of the most beneficial for skin health. A 2012 study supports the view that a diet rich in olive oil can reduce the effects of photoaging on facial skin. The benefits are attributed to monounsaturated fatty acids and compounds like squalene, which may help prevent dryness and damage from free radicals.
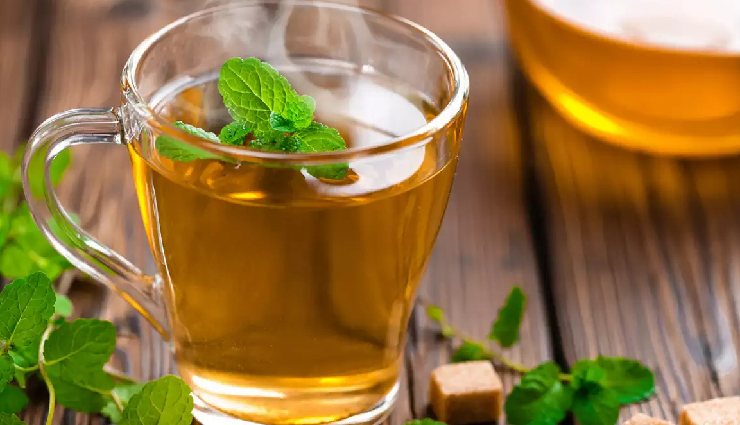

# Green Tea
Green tea is not only a refreshing beverage but also contains compounds that may benefit the skin. According to a 2011 study, green tea is rich in antioxidants called catechins, which enhance blood flow to the skin. Improved circulation ensures that skin cells receive adequate oxygen and nutrients, contributing to their overall health.





