What Is Fungal Acne? Major Causes, Symptoms And Treatments
By: Priyanka Maheshwari Wed, 09 Aug 2023 11:17:03
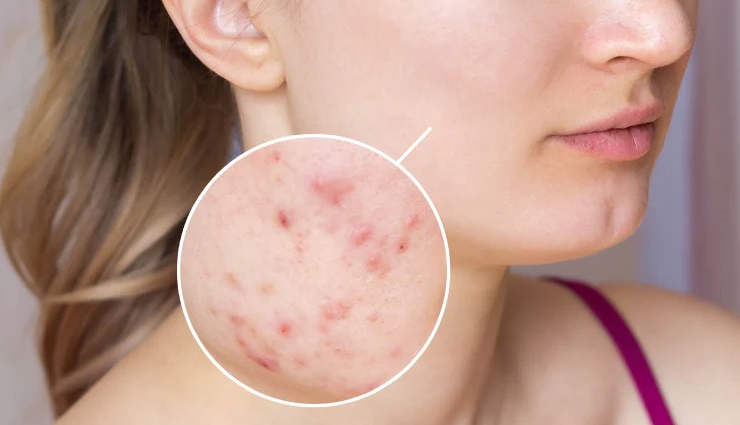
Fungal acne, also known as pityrosporum folliculitis or malassezia folliculitis, is a skin condition that resembles traditional acne but is caused by an overgrowth of yeast-like fungi called Malassezia. While regular acne is primarily caused by the inflammation of hair follicles due to excess oil production and the presence of bacteria, fungal acne is caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeasts within the hair follicles.
The symptoms of fungal acne include:
- Small, uniform, red or skin-colored bumps.
- Itchy or irritated skin.
- Clusters of bumps that resemble acne.
- Rapid spreading and recurrent outbreaks.
Fungal acne tends to occur in areas with a higher density of hair follicles, such as the chest, back, shoulders, and forehead. Unlike traditional acne, fungal acne is not caused by clogged pores, and using typical acne treatments such as benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid may not be effective and can sometimes exacerbate the condition.
Treatment for fungal acne typically involves antifungal medications, such as topical or oral antifungal creams, shampoos, or cleansers containing ingredients like ketoconazole or pyrithione zinc. Maintaining good hygiene, avoiding occlusive or heavily oily products, and making sure to keep the affected areas clean and dry are also important steps in managing fungal acne.
If you suspect you have fungal acne, it's best to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment plan, as other skin conditions can mimic its symptoms.
Major Causes of Fungal Acne
Fungal acne, also known as pityrosporum folliculitis or malassezia folliculitis, is primarily caused by an overgrowth of a specific type of yeast called Malassezia. Here are some major factors that can contribute to the development of fungal acne:
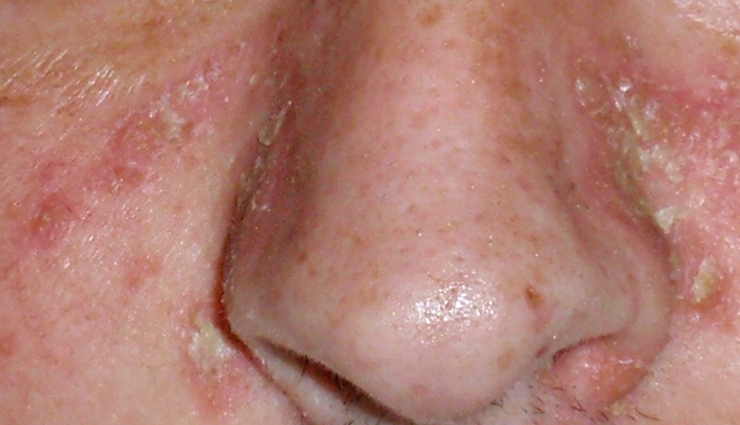
# Malassezia Overgrowth
The primary cause of fungal acne is an overgrowth of the Malassezia yeast on the skin. This yeast is normally present on the skin's surface and is a part of the skin's natural microbiome. However, when it proliferates excessively, it can lead to the development of fungal acne.
# Humid and Warm Environments
Malassezia yeast thrives in warm and humid conditions. These conditions can promote the overgrowth of yeast on the skin, leading to the development of fungal acne. Areas of the body that are covered or prone to sweating, such as the chest, back, and forehead, are commonly affected.

# Excessive Moisture and Sweating
Prolonged moisture and sweating can create an environment conducive to Malassezia overgrowth. Activities that cause excessive sweating or wearing tight clothing that traps moisture against the skin can contribute to the development of fungal acne.
# Occlusive or Heavy Skincare Products
Some skincare and cosmetic products can be comedogenic or occlusive, meaning they can block pores and create an environment where yeast can flourish. Oily or greasy products can also contribute to the growth of Malassezia.
# Antibiotics and Immunosuppression
Long-term use of antibiotics can disrupt the balance of the skin's microbiome, allowing Malassezia to proliferate. Additionally, weakened immune systems due to conditions like HIV or the use of immunosuppressive medications can make individuals more susceptible to fungal infections, including fungal acne.
# Prolonged Antibiotic Use
Antibiotics, particularly broad-spectrum ones, can alter the balance of bacteria on the skin, allowing Malassezia to thrive and cause fungal acne.
# Hot and Humid Climates
Living in regions with hot and humid climates can increase the likelihood of developing fungal acne due to the favorable conditions for Malassezia growth.
# Hormonal Changes
While less common, hormonal fluctuations can potentially play a role in the development of fungal acne. Hormones can influence sebum production and skin conditions, which could indirectly contribute to the overgrowth of Malassezia.
Major Symptoms of Fungal Acne
Fungal acne, also known as pityrosporum folliculitis or malassezia folliculitis, presents with symptoms that can be similar to traditional acne but with some distinguishing features. Here are the major symptoms associated with fungal acne:
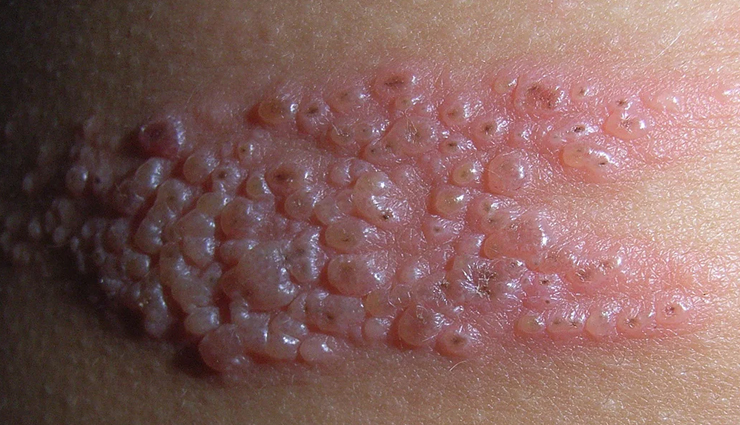
# Clusters of Small Bumps
Fungal acne typically appears as clusters of small, uniform, red or skin-colored bumps. These bumps can resemble traditional acne, but they are generally smaller and more closely spaced. They often appear in groups and may have a distinct pattern.
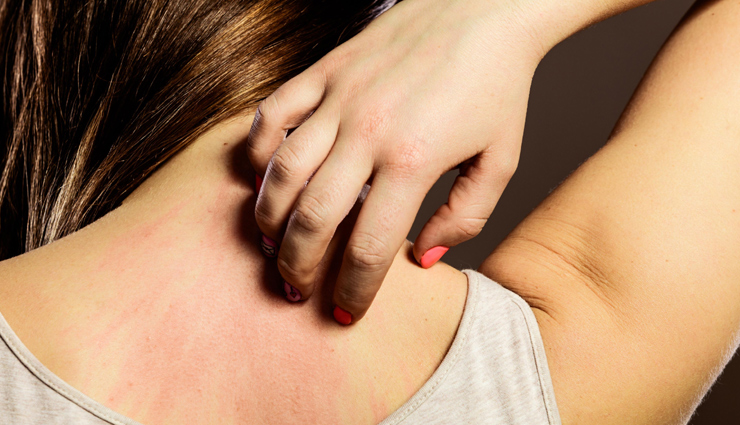
# Itching and Irritation
Fungal acne can be intensely itchy and irritating. The affected areas may feel uncomfortable, and scratching can worsen the condition.
# Uniform Appearance
Unlike regular acne, which can vary in size and shape, fungal acne lesions tend to be quite uniform in size and appearance. This uniformity is due to the fact that fungal acne is caused by an overgrowth of yeast within hair follicles.

# Quick Spreading and Recurrence
Fungal acne can spread rapidly, especially in warm and humid conditions. If left untreated, the clusters of bumps can increase in size and number, leading to more widespread involvement. Additionally, fungal acne can recur if not properly managed, especially if the underlying conditions that promote Malassezia growth are not addressed.
# Location on the Body
Fungal acne most commonly appears on areas of the body with a high density of hair follicles, such as the chest, back, shoulders, and forehead. These areas provide an ideal environment for Malassezia yeast to thrive.
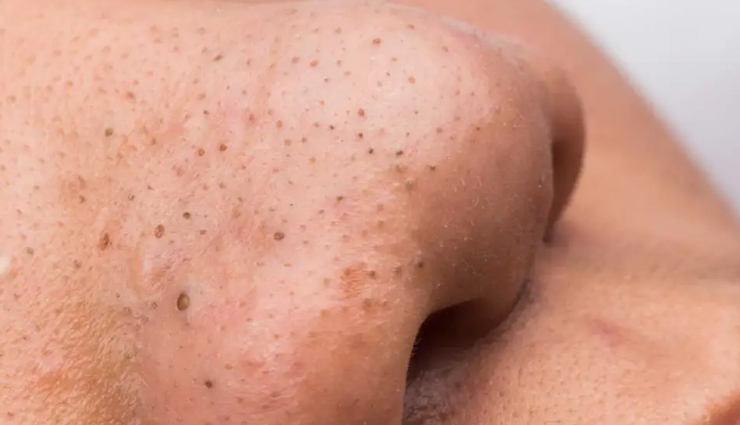
# Lack of Blackheads and Whiteheads
Unlike traditional acne, fungal acne typically does not present with blackheads (open comedones) or whiteheads (closed comedones). Instead, the bumps are often uniform in appearance and lack the presence of the characteristic sebum-filled pores associated with regular acne.
# Absence of Pain or Tenderness
Fungal acne lesions are usually not painful or tender to the touch. Unlike inflamed pimples in traditional acne, which can be sensitive and painful, the bumps in fungal acne are primarily itchy and irritating.
Treatment of Fungal Acne
The treatment of fungal acne, also known as pityrosporum folliculitis or malassezia folliculitis, involves addressing the underlying overgrowth of Malassezia yeast and managing the associated symptoms. Here are some common approaches to treating fungal acne:
# Antifungal Products
The primary goal is to target and reduce the overgrowth of Malassezia yeast. Antifungal treatments can include:
# Topical Antifungal Creams
Over-the-counter or prescription antifungal creams containing ingredients like ketoconazole, clotrimazole, or ciclopirox can be applied directly to the affected areas. These creams help to eliminate the yeast and clear up the bumps.
# Antifungal Shampoos
If the condition is present on the scalp or forehead, using an antifungal shampoo containing ketoconazole or pyrithione zinc can help reduce yeast overgrowth. Leave the shampoo on the affected area for a few minutes before rinsing.
# Cleansing and Hygiene
Proper hygiene practices can help prevent further exacerbation of fungal acne:
# Gentle Cleansing
Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser to keep the affected areas clean. Avoid harsh scrubbing, as it can irritate the skin.
# Avoid Occlusive Products
Use skincare and cosmetic products that are oil-free and non-comedogenic to avoid blocking pores and promoting yeast growth.
# Avoid Moisture and Sweating
Minimize excessive sweating and moisture in the affected areas, as a warm and humid environment can contribute to yeast overgrowth. Wear breathable fabrics and avoid tight clothing.
# Limit Sugar and Carbohydrate Intake
Some research suggests that reducing sugar and carbohydrate consumption may help control Malassezia overgrowth, as these yeasts can thrive on sugars.
# Topical Anti-Inflammatory Products
In cases where the skin is inflamed and itchy, using topical corticosteroids under the guidance of a dermatologist can help reduce inflammation and discomfort. However, these should only be used as directed due to potential side effects with prolonged use.
# Consult a Dermatologis
If over-the-counter treatments are not effective or if the condition is severe, it's recommended to consult a dermatologist. A dermatologist can provide a proper diagnosis, prescribe appropriate medications, and tailor the treatment plan to your specific needs.
# Prescription Medications
In more severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe oral antifungal medications, such as fluconazole or itraconazole, to address the overgrowth of Malassezia yeast from within the body. These medications are usually used when topical treatments alone are insufficient.





