- Home›
- Healthy Living›
- 11 Health Benefits Of Eating Eggs
11 Health Benefits Of Eating Eggs
By: Priyanka Maheshwari Sat, 16 July 2022 08:48:19

What came first the chicken or the egg? We may never know, but we do know there are many reasons to make eggs an essential part of your diet.
Eggs have been a dietary staple since time immemorial and there’s good reason for their continued presence in our menus and meals. Not only do they offer culinary variety hard-boiled eggs, omelets, deviled eggs and then some they are also a source of protein, calcium and several vitamins and nutrients. Here are some of the benefits of incorporating eggs into your diet.

# Growth
When it comes to children, there are always different things that they are told to deter them from eating or drinking something that they should not be eating or drinking at their age. The one that comes to mind is that coffee stunts your growth, right? Eggs do the exact opposite.
Young children, when put on a ‘diet’ of reduced sugar-sweetened foods and a daily egg, can reach a healthy height and not be stunted as they get older.
# Heart Health
Eating an egg a day can do amazing things for limiting the chances of strokes and heart disease. This is because the eggs contain nutrients called betaine and choline. The eggs have to be a steady and consistent part of your diet for them to truly help.
# Rickets and Osteoporosis
Eggs are rich in vitamin D which helps to ward off osteoporosis and rickets. The different ways that the layer chicken is raised can affect the amount of vitamin D they have. Organic (free range) chickens have more than the eggs of chickens that were raised in a factory.

# Duck Eggs
Duck and chicken eggs have a lot of the same nutrients, but duck eggs are bigger. Because duck eggs are bigger, they hold even more nutrients. You should be a little bit more careful with duck eggs because duck eggs contain more cholesterol and fat.

# Cook Well
This is something that is very important. Eggs that are not fully cooked can result in something called salmonella. Salmonella is a kind of food poisoning. You are more likely to gain an illness, rather than much nutrients if you do not cook your eggs.
# Cholesterol
There has been a debate for a while about whether or not the cholesterol in eggs is good or bad. Eggs are high in cholesterol, but also, there are differing opinions on if the cholesterol directly affects the bloodstream or not. There has been no result that explicitly states if does or does not. So just to be safe, it is best not to over do it. In addition the in same cases, eggs have been known to raise the good cholesterol (the HDL).

# Choline
Choline is something that helps to build cell membranes, they make molecules in the brain that help it to know what to do and when, and they have other functions as well. Most people don’t enough choline, so eating an egg is the perfect way to get some.
# Omega-3
Omega-3 is a kind of fatty acid that helps to keep your blood healthy by keeping triglyceride levels down and around where they should be. Keeping the triglycerides down is part of what protects you from heart diseases.

# Protein
While protein is often over eaten in America, what does should not be overlooked. Protein helps you body to rebuild cells and it also keeps you full. Because eggs keep you full for a while and do not have carbs, a lot of people use them as a key part of some diets.
Protein also helps to build muscles which you see people drinking egg shakes in movies (do not drink eggs, it could be very bad for you). They build the muscles while slowing down the amount of muscle loss and how lost it is lost.
# Energy
The vitamins and the minerals in the eggs can induce energy that is made in the cells. Eggs are great to eat before working out to give you a healthy burst of energy, rather than drinking a sugary energy drink.
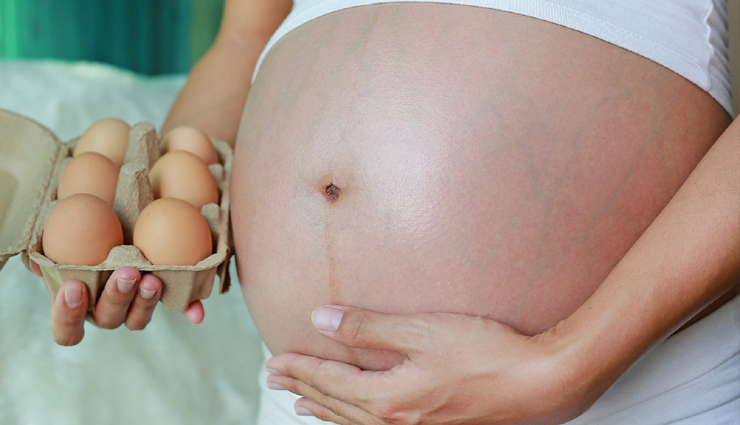

# Pregnancy
There are compounds in eggs that can keep both the mother and the child healthy during pregnancy. The same compound can help to stop the child from developing spina bifida. Pregnant women should try to eat eggs often to improve both their health and the health of their unborn child.





