- Home›
- Healthy Living›
- 11 Strange Side Effects Of Pumpkin Seeds
11 Strange Side Effects Of Pumpkin Seeds
By: Priyanka Maheshwari Mon, 10 July 2023 08:51:26
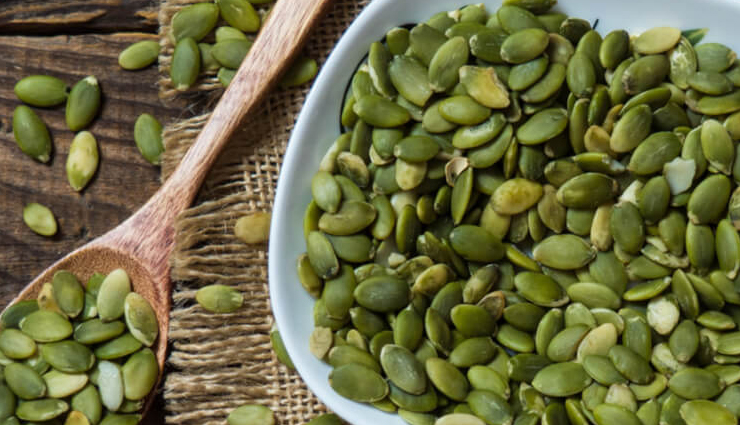

Pumpkin seeds, also known as pepitas, are a popular snack that comes with a myriad of health benefits. They are packed with essential nutrients like magnesium, zinc, and antioxidants, making them a valuable addition to a balanced diet. However, like any food, pumpkin seeds can have unexpected side effects. In this article, we explore 11 strange side effects of pumpkin seeds that you may not be aware of. Let's dive in!

# Flatulence and Digestive Discomfort
One common side effect of consuming pumpkin seeds in excess is flatulence or excessive gas. This is due to the high fiber content present in these seeds. While fiber is beneficial for digestion, consuming large quantities can lead to bloating, flatulence, and even stomach cramps. It is advisable to moderate your pumpkin seed intake if you're experiencing digestive discomfort.
# Allergic Reactions
Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to pumpkin seeds. These reactions can manifest as itching, hives, swelling, or even anaphylaxis in severe cases. If you have a known allergy to other seeds or nuts, it's wise to exercise caution when consuming pumpkin seeds or consult with an allergist.

# Diarrhea
Pumpkin seeds are often consumed for their high fiber content, which aids in maintaining regular bowel movements. However, excessive consumption can lead to loose stools and diarrhea, particularly in individuals with sensitive digestive systems. Balancing your seed intake and ensuring you drink enough fluids can help prevent this uncomfortable side effect.
# Interference with Blood-Thinning Medications
Pumpkin seeds contain vitamin K, which plays a crucial role in blood clotting. If you are taking blood-thinning medications like warfarin, excessive consumption of pumpkin seeds can interfere with the medication's effectiveness. It's crucial to consult your healthcare provider to determine an appropriate intake that won't disrupt your medication regimen.
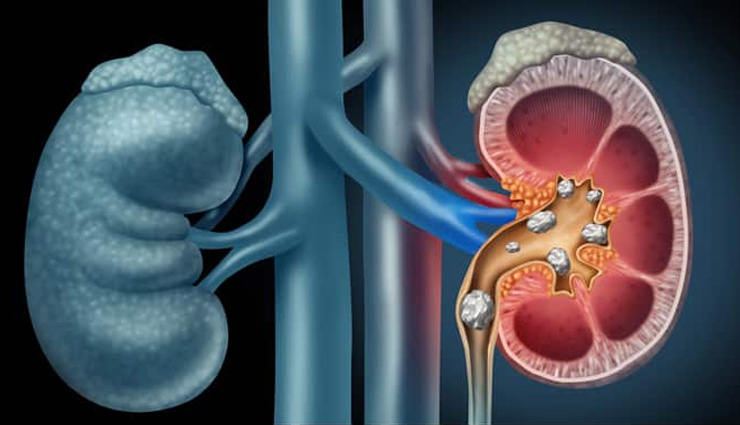
# Kidney Stones
While pumpkin seeds have numerous health benefits, they are also rich in oxalates. In individuals prone to kidney stones, consuming excessive oxalate-rich foods like pumpkin seeds can potentially increase the risk of stone formation. If you have a history of kidney stones, it's advisable to moderate your pumpkin seed consumption and drink plenty of water to reduce the risk.
# Hypoglycemia Risk
Pumpkin seeds have a low glycemic index, which means they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. While this makes them an excellent choice for individuals with diabetes, consuming a large number of pumpkin seeds without balancing them with other foods can lead to a sudden drop in blood sugar levels, resulting in hypoglycemia. It's important to consume them as part of a balanced meal or snack to avoid this potential side effect.

# Weight Gain
Pumpkin seeds are high in calories and healthy fats. While these fats can be beneficial for overall health, excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain if not accounted for in your daily caloric intake. Moderation is key when incorporating pumpkin seeds into your diet, particularly if you're watching your weight.
# Interference with Antidepressant Medications
Some compounds found in pumpkin seeds, such as tryptophan, can potentially interact with certain antidepressant medications. If you are taking medications for depression, consult your healthcare provider to determine whether consuming pumpkin seeds in large amounts may interfere with your medication's effectiveness.

# Hormonal Effects
Pumpkin seeds are known for their high zinc content, which is beneficial for hormone production and regulation. However, consuming excessive amounts of zinc from pumpkin seeds may disrupt hormonal balance, especially in males. It's important to maintain a balanced intake and consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your hormonal health.

# Not Safe For Pregnant And Breastfeeding Women
Pumpkin seeds naturally contain alpha-linolenic acid and DHA, which can be beneficial for breastfeeding mothers. However, it is important to exercise caution and consume them in limited quantities. Pregnant women can also benefit from the nutrient-rich profile of pumpkin seeds, as they provide essential nutrients for prenatal development. Nevertheless, conflicting research exists, and it is crucial to be aware of potential side effects. Therefore, it is advisable to consume pumpkin seeds in moderation and seek guidance from a nutritionist or physician to ensure safety and suitability for individual circumstances.
# Not Safe For People With Low Blood Pressure
Pumpkin seeds possess natural antioxidant properties that can contribute to lowering blood pressure. However, if you have low blood pressure (hypotension) or are currently taking anti-hypertensive medications for high blood pressure, it is recommended to consult with your doctor before incorporating pumpkin seeds into your diet. It is important to discuss the potential complications and risks to ensure the safe and appropriate use of these seeds in your specific situation.

Nutritional profile of pumpkin seeds:
Macronutrients:
Protein: Pumpkin seeds are an excellent plant-based source of protein. They provide about 7 grams of protein per ounce (28 grams).
Fat: Pumpkin seeds are rich in healthy fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. They also contain omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health. However, it's important to note that they are relatively high in calories due to their fat content.
Carbohydrates: Pumpkin seeds contain a moderate amount of carbohydrates, with about 5 grams per ounce. They also provide dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight.
Vitamins:
Vitamin K: Pumpkin seeds are an excellent source of vitamin K, providing around 18% of the recommended daily intake per ounce. Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone health.
Vitamin E: These seeds are also a good source of vitamin E, an antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage.
B vitamins: Pumpkin seeds contain various B vitamins, including thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, and folate. These vitamins play crucial roles in energy production, nerve function, and red blood cell formation.
Minerals:
Magnesium: Pumpkin seeds are particularly rich in magnesium, providing approximately 37% of the recommended daily intake per ounce. Magnesium is involved in hundreds of biochemical reactions in the body and contributes to bone health, energy production, and muscle function.
Zinc: Pumpkin seeds are a notable source of zinc, an essential mineral that supports immune function, wound healing, and proper growth and development.
Iron: These seeds contain iron, which is important for oxygen transport in the body and the prevention of anemia.
Phosphorus, manganese, copper, and potassium are other minerals found in pumpkin seeds in smaller amounts.
Antioxidants:
Pumpkin seeds contain various antioxidants, such as carotenoids and vitamin E, which help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body and protect against chronic diseases.
Other Nutrients:
Phytosterols: Pumpkin seeds are rich in phytosterols, plant compounds that have been associated with reduced LDL cholesterol levels and improved heart health.
Tryptophan: Pumpkin seeds contain tryptophan, an amino acid that is involved in the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that contributes to mood regulation and sleep.





