- Home›
- Healthy Living›
- 8 Common Mistakes To Avoid When Doing Blood Sugar Test
8 Common Mistakes To Avoid When Doing Blood Sugar Test
By: Priyanka Maheshwari Mon, 25 Dec 2023 12:42:27

A blood sugar test, also known as blood glucose testing, is a diagnostic procedure designed to measure the concentration of glucose (sugar) in a person's bloodstream. This test is crucial for assessing how well the body processes glucose, a primary source of energy for cells. Monitoring blood sugar levels is particularly important for individuals with diabetes, a condition characterized by impaired insulin function or production, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
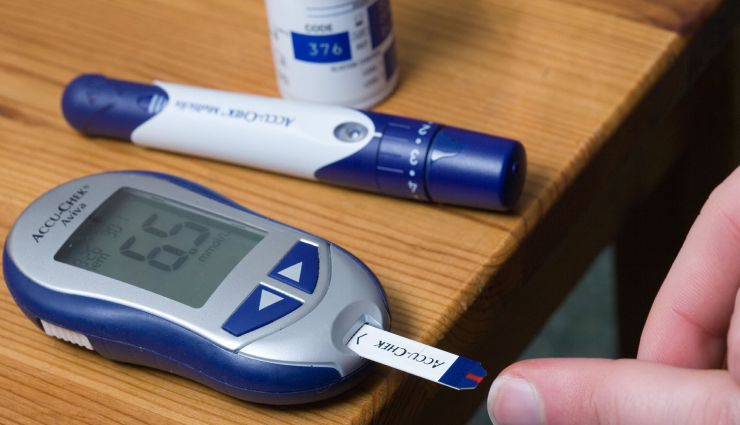
Here's a brief introduction to key aspects of blood sugar testing:
Purpose of Blood Sugar Testing:
- Diabetes Management:
Individuals with diabetes regularly monitor their blood sugar levels to manage and adjust their treatment plans, including medication, diet, and lifestyle choices.
- Early Detection and Prevention:
Blood sugar tests can help identify prediabetes or diabetes in its early stages, allowing for timely interventions to prevent or manage the condition effectively.

Types of Blood Sugar Tests:
- Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS) Test:
Measures glucose levels after an overnight fast. This test helps diagnose diabetes and assesses blood sugar control.
- Postprandial Blood Sugar Test (PPBS):
Measures glucose levels after consuming a meal, providing insights into the body's ability to handle glucose after eating.
- Hemoglobin A1c Test:
Reflects average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It is a valuable tool for long-term glucose monitoring.
- Random Blood Sugar Test:
Involves testing blood glucose levels at any time of the day, without regard to meals. It helps assess immediate glucose levels.

Avoid These Blunders When Checking Your Blood Sugar
# Avoiding regular testing
Maintaining a consistent monitoring schedule is crucial. Neglecting blood sugar tests may lead to missed opportunities to adjust treatment plans, resulting in uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
# Neglecting hand hygiene
Unclean hands can compromise test results. Ensure thorough handwashing before testing to guarantee accurate readings.
# Using expired test strips
Employing test strips beyond their expiration date can produce inaccurate results. Regularly check the expiration date and promptly replace any expired strips.
# Inadequate storage of test strips
Exposure to heat, humidity, or extreme temperatures can compromise the effectiveness of test strips. Store them in a cool, dry place following recommended guidelines.
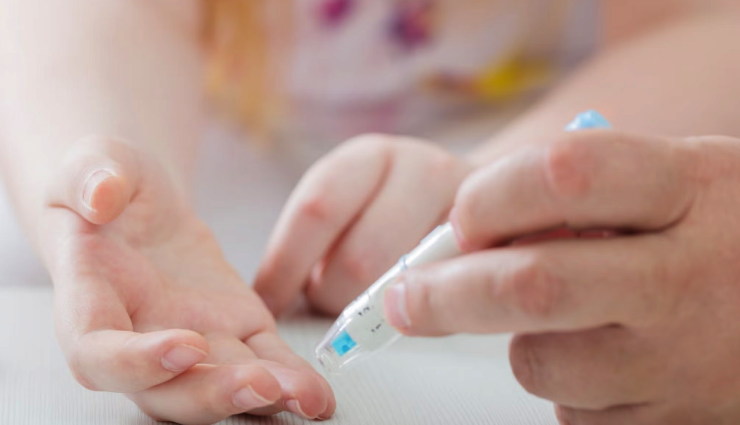
# Disregarding calibration requirements
Neglecting to calibrate your glucose meter, if necessary, can lead to inaccurate readings. Adhere to the manufacturer's guidelines for proper calibration.
# Inconsistent testing times
Conducting blood sugar tests at arbitrary intervals instead of adhering to a consistent schedule can provide an incomplete portrayal of your blood sugar levels. Stick to a routine for more precise monitoring.
# Using the incorrect blood sample
Ensure you use the designated type of blood sample, typically a small drop from the fingertip, as specified by your glucose meter.
# Overlooking external factors
External elements such as stress, illness, or recent exercise can influence blood sugar levels. Consider these factors when interpreting results to gain a more accurate understanding.





