- Home›
- Healthy Living›
- 11 Harmful Myths About Diabetes And Provide You With Accurate Information
11 Harmful Myths About Diabetes And Provide You With Accurate Information
By: Priyanka Maheshwari Sat, 03 Feb 2024 09:38:57
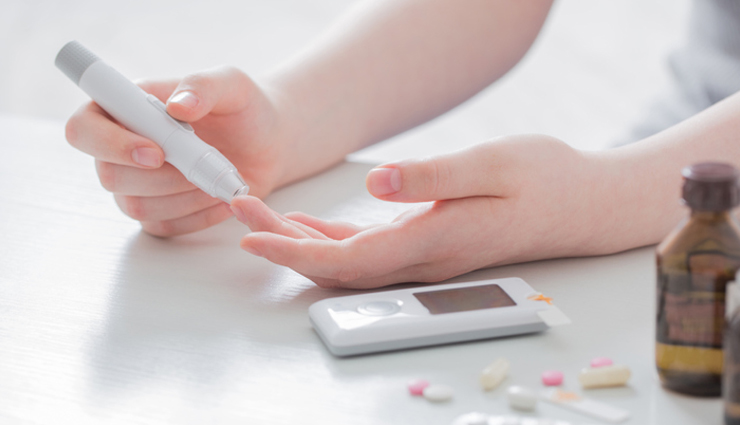

Diabetes, a persistent health condition impacting millions globally, is surrounded by numerous misconceptions and myths. This misinformation can result in confusion. In this context, we aim to dispel 11 detrimental myths associated with diabetes, offering accurate insights to enhance your understanding of this condition.
Harmful Myths About Diabetes
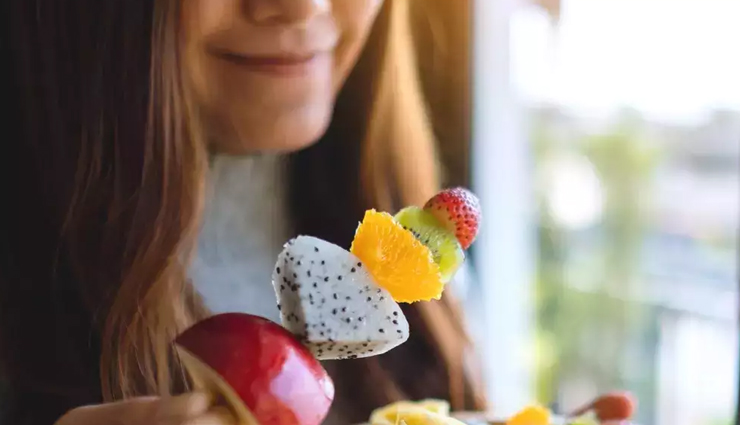

# The misconception that individuals with diabetes should avoid consuming fruits persists, citing their natural sugar content. However, fruits offer vital vitamins, minerals, and fiber with a low glycemic index, minimally affecting blood sugar levels. It's crucial to practice moderation and consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian experienced in diabetes management for personalized guidance on fruit consumption.
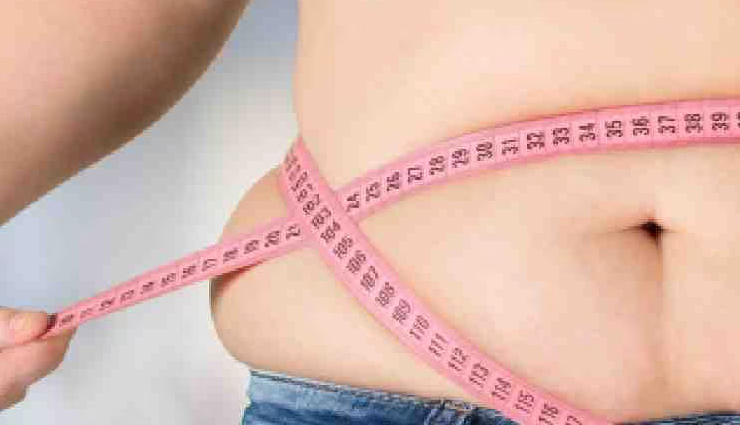

# A prevailing myth suggests that diabetes is caused by sugar intake. In reality, moderate sugar consumption doesn't directly lead to diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition, while type 2 diabetes is influenced by genetic and lifestyle factors such as obesity, inactivity, and poor dietary choices. While sugar doesn't cause diabetes, excessive intake can contribute to weight gain, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
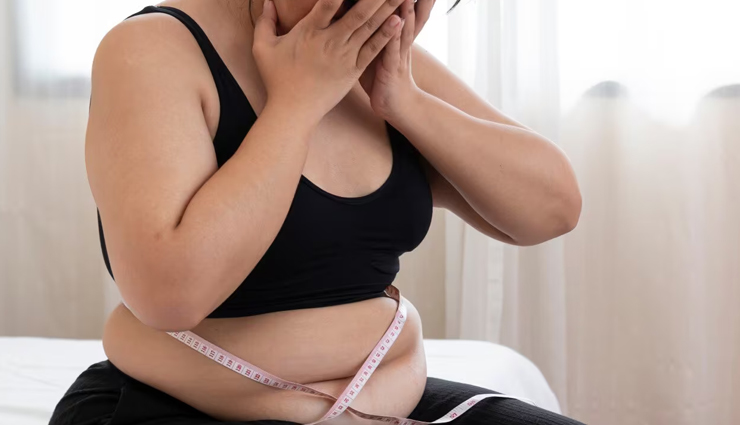

# While obesity is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, it doesn't exclusively affect overweight individuals. Genetics, age, and ethnicity also play significant roles. Thin individuals can develop type 2 diabetes, emphasizing the importance of weight loss efforts for those carrying extra weight. Each kilogram lost correlates with a 16% reduction in the risk of type 2 diabetes.

# The notion that individuals with diabetes must completely avoid sweets is inaccurate. Incorporating sweet treats into a balanced diet is possible with moderation. Monitoring carbohydrate intake and choosing healthier alternatives, like fresh fruits or sugar-free options, is essential. Collaboration with a registered dietitian can aid in creating a controlled meal plan inclusive of favorite treats.

# Moderate alcohol consumption is generally safe for individuals with diabetes. However, alcohol affects blood sugar levels, and excessive intake can lead to hypoglycemia. Therefore, moderation, regular blood sugar monitoring, and consuming a balanced meal alongside alcohol are crucial for individuals with diabetes. Consultation with a doctor is advisable for any concerns.

# A misconception that a specific diabetes diet is mandatory persists. Instead, a balanced eating plan should focus on diverse foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Effective blood sugar management relies on portion control and monitoring carbohydrate intake, allowing flexibility in food choices.
# The belief in a "special" diabetes diet is unfounded. A well-balanced, healthy diet emphasizing whole foods and portion control suits diabetes management. This approach allows for variety in food choices while prioritizing nutrient-dense options to control blood sugar levels and promote overall health.
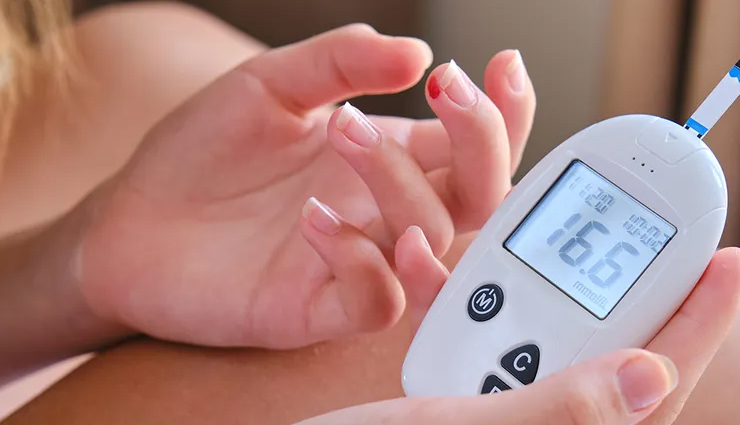
# The myth that type 2 diabetes is less severe than type 1 diabetes is incorrect. While their origins differ, both require regular blood sugar monitoring, a healthy lifestyle, and appropriate medical care for optimal management. The seriousness of diabetes depends on effective control, emphasizing the need for individuals to actively engage in their treatment plans.
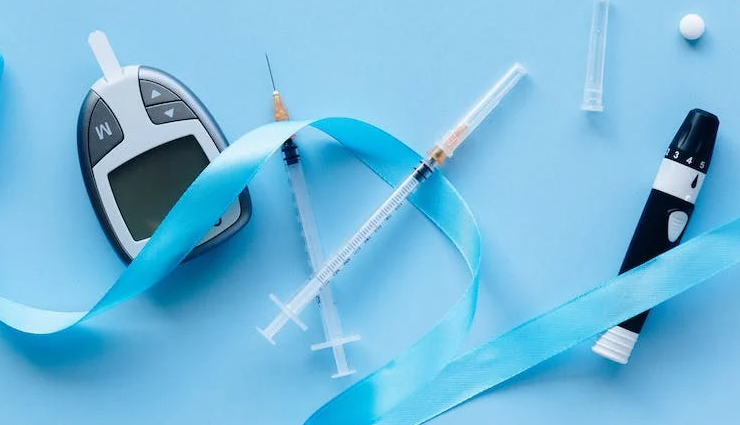
# Diabetes management doesn't universally require insulin. While type 1 diabetes necessitates insulin injections, type 2 diabetes often responds to lifestyle changes, weight management, and oral medications. Following a doctor's prescribed treatment plan is crucial, whether it involves insulin or alternative approaches.
# Contrary to misconceptions, insulin is a safe and vital medication for managing diabetes. It effectively regulates blood sugar levels, preventing complications associated with hyperglycemia. When used under medical guidance, insulin is a beneficial treatment option, ensuring the well-being of individuals with diabetes.
# The belief that the absence of symptoms implies the absence of diabetes is inaccurate. Diabetes can develop gradually, with early signs often unnoticed or mistaken for other issues. Regular check-ups and screenings are crucial, especially for those with risk factors, allowing for early detection and intervention to prevent the progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes. Relying on symptoms alone may lead to missed opportunities for timely intervention, particularly for individuals with a family history of diabetes.





