- Home›
- Healthy Living›
- 13 Least Known Health Benefits Of Breast-feeding For A Baby
13 Least Known Health Benefits Of Breast-feeding For A Baby
By: Priyanka Maheshwari Thu, 24 Aug 2023 3:32:17
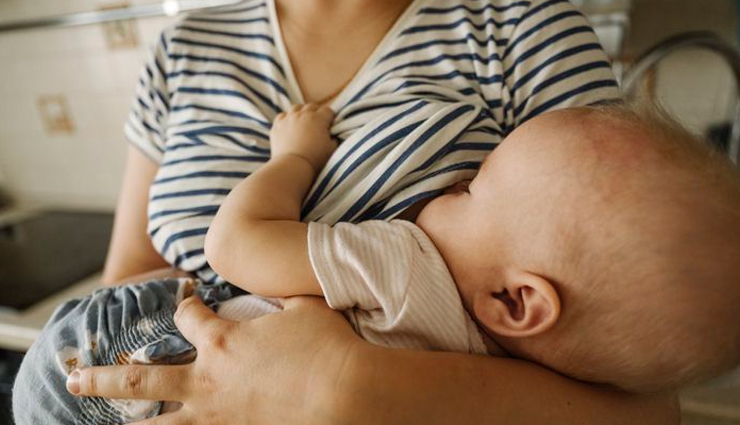

Breastfeeding is a natural and vital process through which a mother provides essential nutrition and nurturing to her newborn or infant. It involves the act of feeding the baby with breast milk produced by the mother's mammary glands. Breast milk is often referred to as "liquid gold" due to its numerous health benefits and nutritional value for the infant.
The act of breastfeeding goes beyond just providing sustenance; it also establishes a strong emotional and bonding connection between the mother and her baby. This physical closeness fosters a sense of security, comfort, and warmth that can contribute significantly to the baby's emotional well-being.
Breast milk is a unique and complex fluid that changes in composition as the baby grows, adapting to the infant's changing nutritional needs. It contains a perfect balance of proteins, fats, vitamins, and antibodies that help protect the baby from infections and diseases. These antibodies and other bioactive components in breast milk contribute to the infant's developing immune system, promoting long-term health.
Moreover, breastfeeding has benefits for the mother as well. It helps the uterus contract after childbirth, aiding in the process of returning to pre-pregnancy size. It can also assist in postpartum weight loss and reduce the risk of certain health issues for the mother, such as breast and ovarian cancer.
However, it's important to note that breastfeeding is a personal choice, and various factors can influence a mother's decision, including her health, lifestyle, and circumstances. Some women may choose not to breastfeed, while others may face challenges that make breastfeeding difficult. In cases where breastfeeding isn't possible, formula feeding can also provide adequate nutrition for the baby.

# Enhanced Cognitive Abilities
Studies indicate that infants who are nourished with breast milk rather than formula tend to exhibit higher levels of intelligence quotient (IQ) during their developmental years and perform better on IQ tests as they progress into school age. Additionally, a connection has been established between the duration of breastfeeding and IQ levels. Infants who are breastfed through their later stages of infancy and into toddlerhood demonstrate elevated IQ scores.
# Promotion of Optimal Brain Size
As the baby undergoes growth, so does the brain in relation to the body. Breastfeeding plays a pivotal role in ensuring the proper and proportional development of the baby's brain, aligning its size appropriately with the baby's age.
# Enhanced Neuronal Health
Infants who are exclusively breastfed exhibit a higher concentration of white matter tissue within the brain. White matter comprises elongated neuronal cells that facilitate inter-brain coordination. This white matter is crucial in influencing the caliber of cognitive processes and thought patterns. Breastfed infants can manifest up to 30% more white matter than their counterparts who are not exclusively breastfed or are formula-fed.
# Acceleration of Brain Maturation in Premature Babies
Breast milk expedites the maturation of the brains of preterm infants, mitigating the risk of cognitive developmental delays. Such infants are also less prone to experiencing psychiatric disorders in later stages of life.

# Diminished Risk of ADHD
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a psychological condition characterized by behavioral challenges. The condition lacks a definitive cure and necessitates lifelong management through medication or alternative therapeutic approaches. Infants who are exclusively breastfed for at least six months and beyond display a reduced likelihood of developing ADHD. While the exact mechanism through which breast milk guards against ADHD remains unknown, it is plausible that the overall cognitive benefits of breast milk contribute to this protective effect.
# Confers Defense Against Common Ailments
Breast milk is rich in a variety of antibodies, including those that combat common illnesses like the common cold. For instance, if a mother is dealing with a common cold, she naturally imparts her immunity to her baby through breastfeeding. This practice shields against bacterial infections such as bacterial meningitis and pneumonia.
# Safeguards Against Select Viral Infections
Breast milk offers protection against viruses like the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and varicella-zoster, which is responsible for chickenpox and shingles. Experts underline that if a mother has experienced chickenpox, she indirectly bestows viral immunity upon her baby. Although this passive immunity might not ensure complete protection, it substantially diminishes the likelihood of the baby contracting the illness.
# Promotes the Proliferation of Beneficial Gut Bacteria
The small intestines of infants contain probiotic bacteria present from birth. However, the population of these beneficial bacteria is initially low. Specific sugars and fats in breast milk foster the growth of these advantageous bacteria. A robust community of intestinal bacteria safeguards against invasive microbes such as E. coli.

# Reduces Allergy and Autoimmune Disease Risks
Breastfed infants exhibit a lower susceptibility to allergic reactions compared to those fed with formula. Immunoglobulins present in breast milk educate the infant's immune system to adeptly differentiate between harmful pathogens and harmless proteins. Consequently, the infant becomes less vulnerable to allergy-related conditions such as asthma. Additionally, the risk of other autoimmune diseases like Crohn's disease is also reduced.
# Mitigates the Risk of SIDS, Leukemia, and Diabetes
Breastfed babies have a decreased likelihood of experiencing sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), certain cancers like leukemia, as well as type 1 and type 2 diabetes.

# Diminished Likelihood of Obesity
Breastfed babies exhibit a reduced occurrence of obesity both during their toddler years and into later stages of life. This not only implies that maintaining a healthy weight is easier for the infant in the present, but also holds significance for their future well-being.
# Facilitates Timely Growth and Progression
Achieving specific developmental milestones is crucial for a baby's normative growth. Breastfed infants tend to experience smoother physical growth and achieve these milestones on schedule, setting them apart from exclusively formula-fed infants.
# Enhances Dental Development and Minimizes Dental Issues
Improved development of primary teeth, also known as deciduous teeth, is observed in breastfed infants, accompanied by fewer complications. Direct breastfeeding contributes to a reduced risk of bottle-induced tooth decay. Furthermore, the sugars present in breast milk are less likely to negatively impact the baby's teeth, unlike the sugars found in formula.





