- Home›
- Healthy Living›
- Which Is Better For Health- Nuts Or Seeds?
Which Is Better For Health- Nuts Or Seeds?
By: Priyanka Maheshwari Mon, 12 Aug 2024 11:14:01
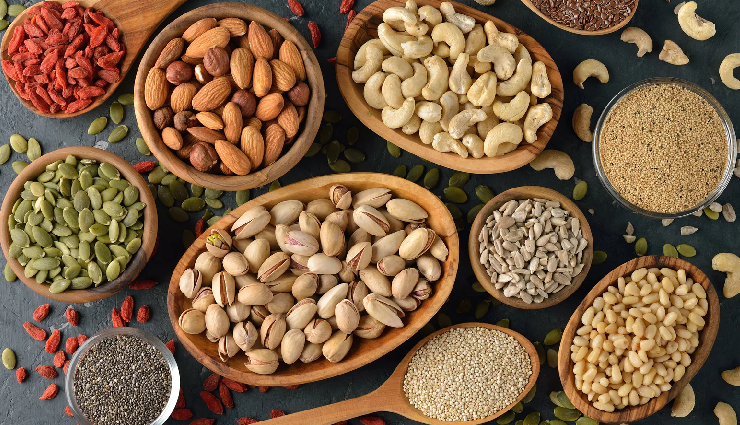

Nuts and seeds are powerhouse foods packed with essential nutrients that contribute significantly to overall health and well-being. These small yet mighty foods are rich in healthy fats, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them valuable additions to any diet.
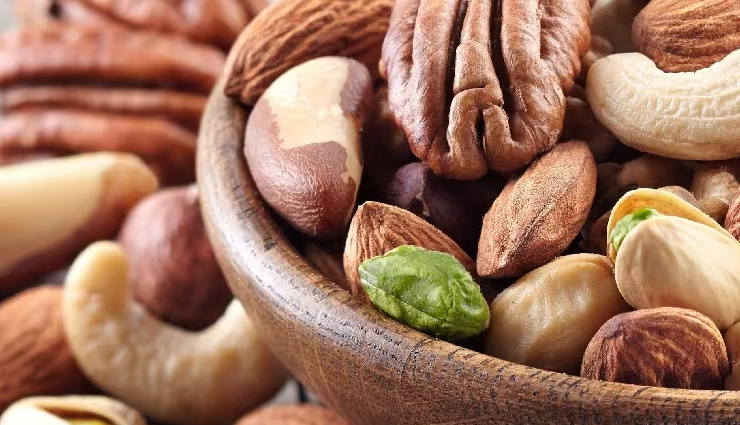

Nuts:
Nuts, such as almonds, walnuts, cashews, and hazelnuts, are known for their high content of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are heart-healthy and can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases. They also provide a substantial amount of plant-based protein, making them a great option for vegetarians and vegans. Additionally, nuts are abundant in antioxidants, which combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body, supporting overall health.
Nutritional Profile of Nuts
Calories: Nuts are generally high in calories, with a typical serving (about 1 ounce or 28 grams) providing 150–200 calories.
Healthy Fats:
Monounsaturated Fats: Almonds, cashews, and hazelnuts are particularly high in these heart-healthy fats.
Polyunsaturated Fats: Walnuts and pine nuts are rich in polyunsaturated fats, including omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids.
Protein: Nuts are a good source of plant-based protein, typically offering 4–7 grams per ounce. Peanuts (technically a legume) and almonds are particularly high in protein.
Fiber: Most nuts contain about 2–3 grams of fiber per ounce, which aids digestion and supports gut health.
Vitamins:
Vitamin E: Almonds are especially rich in vitamin E, an antioxidant that supports skin health and immune function.
B Vitamins: Many nuts, including pistachios and cashews, provide B vitamins like folate and niacin, which are essential for energy metabolism.
Minerals:
Magnesium: Nuts like cashews and almonds are excellent sources of magnesium, which is important for muscle function and bone health.
Zinc: Cashews and pine nuts are good sources of zinc, vital for immune health and wound healing.
Calcium: Almonds are one of the best nut sources of calcium, important for bone health.
Antioxidants: Walnuts, pecans, and chestnuts are particularly high in antioxidants, including polyphenols, which protect against oxidative stress.
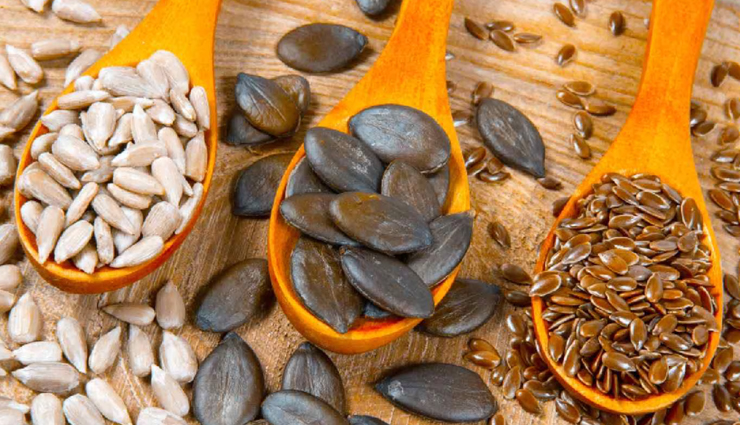

Seeds:
Seeds, including flaxseeds, chia seeds, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds, are equally impressive in their nutritional profile. They are excellent sources of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy gut. Many seeds, like flax and chia, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, essential for brain function and reducing inflammation. Seeds also offer a wealth of minerals, such as magnesium, zinc, and iron, which are crucial for various bodily functions, including immune support and energy production.
Nutritional Profile of Seeds
Calories: Seeds are also calorie-dense, with most providing 150–200 calories per ounce.
Healthy Fats:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Flaxseeds and chia seeds are rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid that supports heart health.
Polyunsaturated Fats: Seeds like sunflower and pumpkin seeds contain omega-6 fatty acids.
Protein: Seeds typically provide 5–9 grams of protein per ounce. Hemp seeds and pumpkin seeds are particularly high in protein, with hemp seeds offering complete protein with all nine essential amino acids.
Fiber: Seeds are an excellent source of dietary fiber, often providing 3–5 grams per ounce. Chia seeds are particularly high in fiber, with around 10 grams per ounce.
Vitamins:
Vitamin E: Sunflower seeds are especially rich in vitamin E, which acts as an antioxidant.
B Vitamins: Many seeds, such as flaxseeds and pumpkin seeds, contain B vitamins, including folate and niacin.
Minerals:
Magnesium: Pumpkin seeds are exceptionally high in magnesium, contributing to muscle function, energy production, and bone health.
Zinc: Pumpkin seeds are also a good source of zinc, important for immune function.
Iron: Seeds like sesame and pumpkin seeds are rich in iron, crucial for oxygen transport in the body.
Health Benefits
Nuts
# Heart Health
- Healthy Fats: Nuts are high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels while increasing HDL (good) cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: The omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants in nuts can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
- Blood Pressure: Regular nut consumption has been linked to lower blood pressure, which is beneficial for overall cardiovascular health.
# Weight Management
- Satiety: Nuts are high in protein and fiber, which can help you feel full and satisfied, potentially reducing overall calorie intake and aiding in weight management.
- Metabolism: The fats in nuts are not fully absorbed by the body, meaning they have a lower effective calorie content than what is listed on the nutrition label.
# Blood Sugar Control
- Glycemic Control: Nuts have a low glycemic index, meaning they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. This makes them a suitable snack for people with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar.
- Insulin Sensitivity: Nuts can improve insulin sensitivity, which is beneficial for blood sugar management.
# Brain Health
- Cognitive Function: Nuts, especially walnuts, are high in DHA, an omega-3 fatty acid that supports brain health and cognitive function. Regular consumption is associated with better memory and cognitive performance.
- Antioxidants: Nuts contain antioxidants like vitamin E, which protect brain cells from oxidative damage and may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
# Digestive Health
- Fiber: Nuts are a good source of dietary fiber, which promotes healthy digestion and regular bowel movements.
- Gut Health: The fiber in nuts can also act as a prebiotic, supporting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
# Bone Health
- Minerals: Nuts like almonds are rich in calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, all of which are essential for maintaining strong and healthy bones.
- Bone Density: Regular nut consumption has been linked to improved bone density and a lower risk of osteoporosis.
# Skin Health
- Vitamin E: Nuts such as almonds are high in vitamin E, an antioxidant that helps protect the skin from oxidative damage, supports skin health, and may help prevent signs of aging.
- Healthy Fats: The healthy fats in nuts can help maintain skin hydration and elasticity.
# Cancer Prevention
- Antioxidants: Nuts contain antioxidants like vitamin E, selenium, and phytosterols, which help protect cells from damage and may reduce the risk of certain cancers.
- Anti-Cancer Compounds: Some studies suggest that the regular consumption of nuts is associated with a lower risk of cancers, including colorectal and breast cancer.
# Immune Support
- Vitamins and Minerals: Nuts are rich in essential vitamins and minerals, such as zinc and selenium, which play crucial roles in maintaining a healthy immune system.

Seeds
# Heart Health
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Seeds like flaxseeds and chia seeds are rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of plant-based omega-3 fatty acid that supports heart health by reducing inflammation and lowering blood pressure.
- Cholesterol Levels: Seeds can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol and increase HDL (good) cholesterol, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Antioxidants: Seeds contain antioxidants such as vitamin E and phytosterols, which help protect the heart by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
# Digestive Health
- Fiber Content: Seeds are an excellent source of dietary fiber, which promotes healthy digestion, regular bowel movements, and prevents constipation.
- Prebiotic Properties: The fiber in seeds can act as a prebiotic, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria and supporting a healthy digestive system.
# Weight Management
- Satiety: Seeds are high in fiber and protein, which can help you feel full and satisfied, potentially reducing overall calorie intake and aiding in weight management.
- Nutrient Density: Seeds provide essential nutrients with relatively few calories, making them a filling and nutritious snack.
# Bone Health
- Minerals: Seeds such as sesame seeds and chia seeds are rich in minerals like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, which are crucial for maintaining strong and healthy bones.
- Bone Density: Regular consumption of seeds can contribute to improved bone density and lower the risk of osteoporosis.
# Blood Sugar Control
- Low Glycemic Index: Seeds have a low glycemic index, meaning they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels, making them a good choice for people with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar.
- Insulin Sensitivity: Some seeds, like chia and flaxseeds, may improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels.
# Brain Health
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Seeds like flaxseeds and chia seeds are high in ALA, which supports brain health, cognitive function, and may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Antioxidants: Seeds contain antioxidants that help protect brain cells from oxidative damage and support overall brain health.
# Skin Health
- Healthy Fats: The healthy fats in seeds, including omega-3 fatty acids, help maintain skin hydration and elasticity.
- Vitamin E: Many seeds, such as sunflower seeds, are rich in vitamin E, which acts as an antioxidant and supports skin health.
# Immune Support
- Vitamins and Minerals: Seeds provide essential nutrients such as zinc, selenium, and vitamin E, which are important for maintaining a healthy immune system and supporting immune function.
# Hormonal Balance
- Phytoestrogens: Seeds like flaxseeds contain lignans, which are phytoestrogens that can help balance hormones and may reduce symptoms of menopause.
# Anti-Inflammatory Properties
- Omega-3s and Antioxidants: The omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants in seeds can help reduce inflammation throughout the body, potentially lowering the risk of chronic inflammatory conditions.
Both nuts and seeds are incredibly nutritious, offering a combination of healthy fats, protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Incorporating a variety of nuts and seeds into your diet can help ensure you receive a wide range of these essential nutrients, supporting overall health and well-being.
Incorporating a variety of nuts and seeds into your daily diet can be an effective strategy for boosting nutrient intake and supporting overall health. Whether eaten on their own, sprinkled over salads, blended into smoothies, or included in baked goods, nuts and seeds offer a versatile and delicious way to enhance your diet and improve your well-being.





