- Home›
- Healthy Living›
- Smoking And Heart Health: Know How Tobacco Use Damages Your Cardiovascular System
Smoking And Heart Health: Know How Tobacco Use Damages Your Cardiovascular System
By: Priyanka Maheshwari Wed, 26 Apr 2023 12:41:37
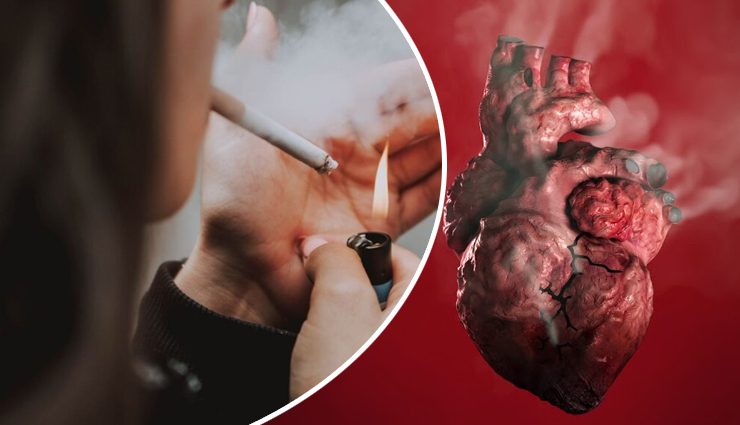
Smoking is one of the leading causes of cardiovascular disease worldwide. It is responsible for an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Smoking not only harms the lungs but also damages the heart and blood vessels, leading to chronic and life-threatening conditions.

How does smoking affect the heart?
Smoking cigarettes causes the heart to work harder and reduces the amount of oxygen that can reach the heart muscle. This increases the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, which can lead to chest pain, heart attack, or even death.
Nicotine, the addictive substance found in cigarettes, narrows the blood vessels, making it harder for blood to flow freely through the body. This increases blood pressure and puts a strain on the heart, which has to work harder to pump blood around the body. Over time, this extra stress on the heart can cause it to become weaker and less efficient.
Smoking also increases the levels of carbon monoxide in the blood, which reduces the amount of oxygen that can be carried by the blood. This puts further strain on the heart, which has to work even harder to deliver enough oxygen to the body's organs and tissues.
The harmful effects of smoking on the heart can start to develop in as little as 20 minutes after smoking a cigarette. Over time, the damage caused by smoking can become irreversible and increase the risk of developing serious cardiovascular diseases.

Coronary artery disease
Smoking is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition in which the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed and hardened due to a buildup of plaque. CAD is the most common type of heart disease and a leading cause of death worldwide.
When you smoke, the chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the lining of the blood vessels, making them more susceptible to the buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) in the inner walls of the arteries. This buildup of plaque narrows the arteries, which reduces blood flow to the heart muscle. Over time, this can lead to chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms of CAD.
Smoking also increases the risk of blood clots, which can further narrow the arteries and block blood flow to the heart. This can lead to a heart attack, a condition in which the blood supply to the heart muscle is suddenly blocked, causing permanent damage to the heart muscle.
Research has shown that smoking increases the risk of CAD by 2-4 times compared to non-smokers, and this risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the duration of smoking. In fact, smokers who quit can reduce their risk of CAD by half within one year of quitting.

Stroke
Smoking is a significant risk factor for stroke, which occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or reduced, leading to brain damage and potentially permanent disability or death. Stroke can be caused by either a blockage of blood flow (ischemic stroke) or bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke).
The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the blood vessels in the brain, making them more prone to developing blood clots or rupturing, which can lead to stroke. Smoking also increases the risk of atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can further increase the risk of stroke.
Research has shown that smoking increases the risk of stroke by two to four times compared to non-smokers. The risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the duration of smoking. Secondhand smoke exposure also increases the risk of stroke.

Peripheral artery disease:
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a condition in which the blood vessels that supply blood to the legs and feet become narrowed or blocked, leading to reduced blood flow to these areas. Smoking is a significant risk factor for PAD, as it can cause damage to the blood vessels and increase the risk of atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
When you smoke, the chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the blood vessels, causing inflammation and reducing their ability to function properly. This damage can make the blood vessels more susceptible to atherosclerosis, which can further narrow or block the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the legs and feet.
Smoking also increases the risk of blood clots, which can further narrow or block the arteries, leading to PAD. The nicotine in tobacco smoke can cause the blood vessels to constrict, which can further reduce blood flow to the legs and feet.

Aortic aneurysm
An aortic aneurysm is a condition in which the wall of the aorta, the largest artery in the body, becomes weakened and bulges out, which can potentially lead to a life-threatening rupture. Smoking is a significant risk factor for aortic aneurysm, as it can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
When you smoke, the chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the blood vessels, causing inflammation and reducing their ability to function properly. This damage can make the blood vessels more susceptible to atherosclerosis, which can lead to the development of an aortic aneurysm. Smoking also increases blood pressure and heart rate, which can further increase the risk of aortic aneurysm.

How to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases caused by smoking?
The best way to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases caused by smoking is to quit smoking. This can be challenging, but it is possible with the help of a support system, such as a doctor, counselor, or a quit-smoking program.
Other ways to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases include:
- Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Regular physical activity to improve cardiovascular health.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Managing stress levels through relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga.
- Avoiding exposure to second-hand smoke.
Conclusion
Smoking is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease worldwide. It damages the heart and blood vessels, leading to serious conditions such as heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. Quitting smoking is the best way to reduce the risk of developing these diseases. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, it is possible to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases caused by smoking and live a longer, healthier life.





