- Home›
- Healthy Living›
- The Vitality Of Vitamin B12: Health Benefits And Food Sources
The Vitality Of Vitamin B12: Health Benefits And Food Sources
By: Priyanka Maheshwari Tue, 04 July 2023 10:52:26

Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. This water-soluble vitamin is necessary for various bodily functions, including red blood cell formation, neurological health, DNA synthesis, and energy production. In this article, we will explore the benefits of vitamin B12 for health and highlight food sources rich in this vital nutrient.
# Improved Red Blood Cell Production
Vitamin B12 is necessary for the production of healthy red blood cells. It aids in the formation of DNA and helps in the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Adequate levels of vitamin B12 are essential for preventing megaloblastic anemia, a condition characterized by the production of large, immature red blood cells.
# Enhanced Neurological Function
Vitamin B12 plays a significant role in maintaining a healthy nervous system. It supports the proper functioning of nerve cells and aids in the synthesis of myelin, a protective covering that surrounds nerve fibers. Adequate vitamin B12 levels are crucial for optimal neurological function, including cognitive performance and memory.

# Energy Metabolism
Vitamin B12 is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. It assists in converting food into energy, making it vital for maintaining overall energy levels. Sufficient vitamin B12 intake can help prevent feelings of fatigue and support a healthy metabolism.

# Mood Regulation
Vitamin B12 is linked to mood regulation and mental well-being. It plays a role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are involved in mood regulation. Adequate levels of vitamin B12 are essential for maintaining a positive mood and preventing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
# Cardiovascular Health
Vitamin B12 contributes to cardiovascular health by helping to regulate homocysteine levels in the blood. Elevated levels of homocysteine are associated with an increased risk of heart disease. Vitamin B12, along with other B vitamins, assists in converting homocysteine into methionine, an essential amino acid, thus supporting heart health.
Food Sources of Vitamin B12:
To ensure sufficient intake of vitamin B12, include the following food sources in your diet:
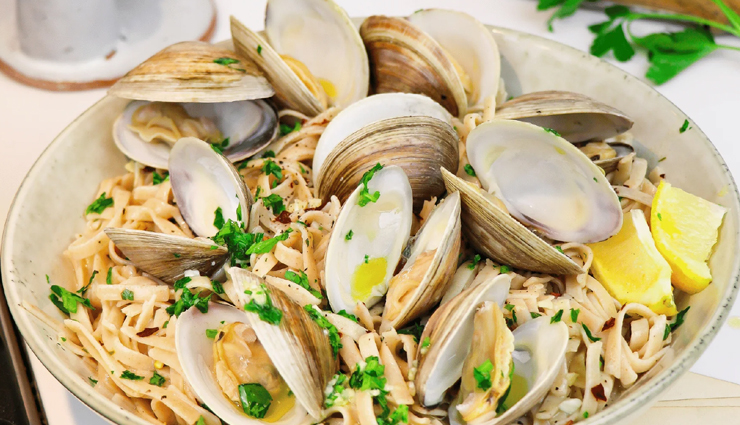

# Clams
Clams are exceptionally rich in vitamin B12, making them one of the best food sources. Just 100 grams of cooked clams can provide several times the daily recommended intake of vitamin B12.
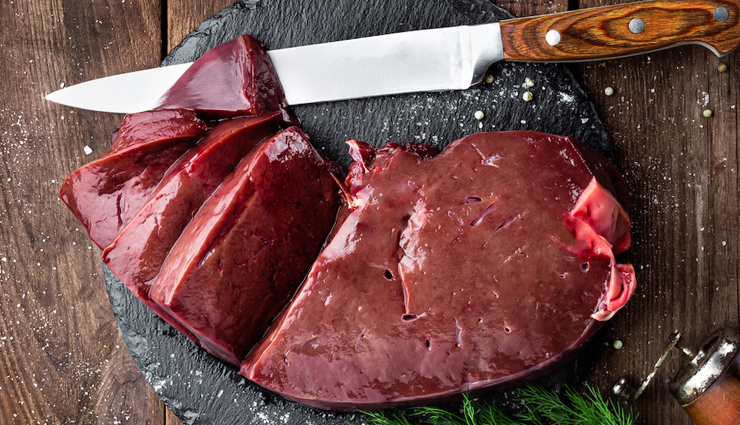

# Liver
Liver, particularly beef liver, is a nutrient powerhouse, including being a great source of vitamin B12. It is also rich in other essential nutrients like iron and vitamin A.
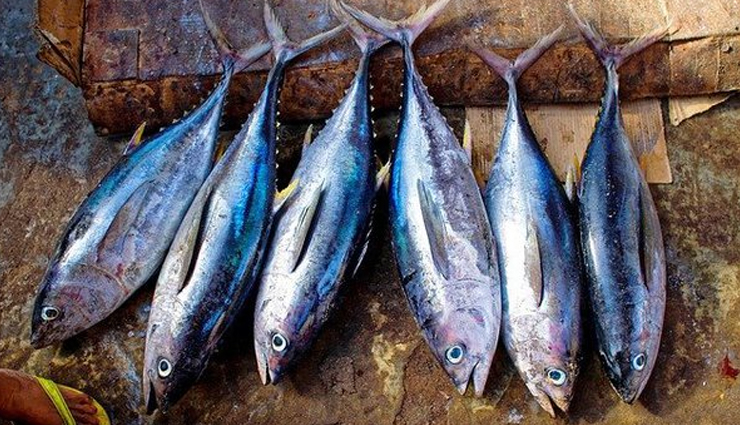

# Fish
Certain fish species are excellent sources of vitamin B12. Mackerel, trout, salmon, and tuna are particularly noteworthy. Opt for wild-caught varieties when possible for maximum nutritional benefits.
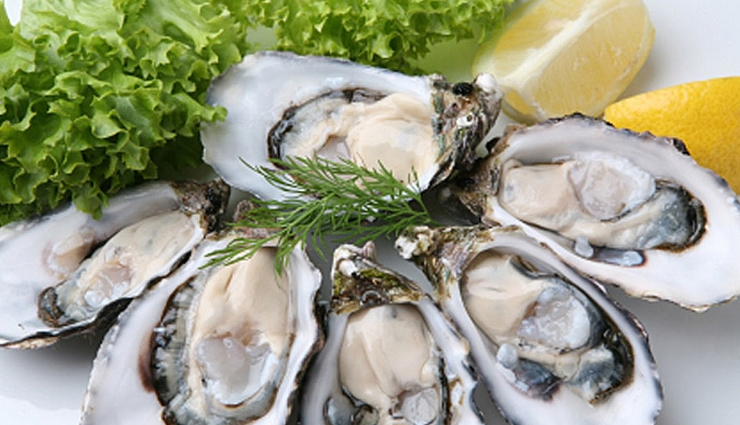

# Shellfish
In addition to clams, other shellfish like mussels, oysters, and crab contain significant amounts of vitamin B12. They make a delicious addition to seafood dishes while providing important nutrients.
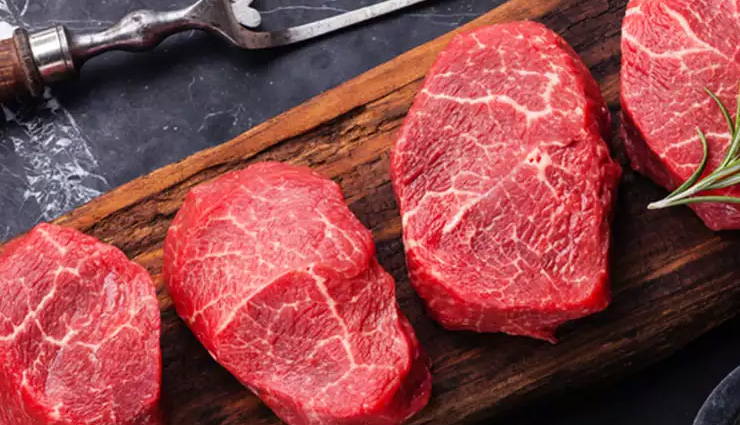

# Red Meat
Beef, lamb, and pork are good sources of vitamin B12. Opt for lean cuts and moderate your consumption for a well-balanced diet.
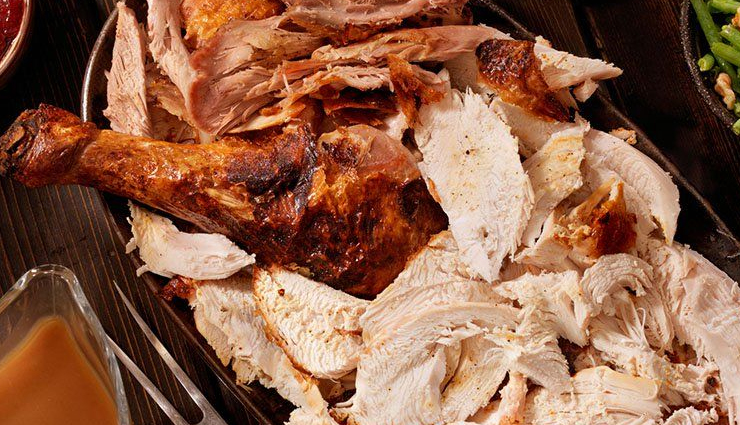

# Poultry
Chicken and turkey, especially the darker meat and organ meats like giblets, contain vitamin B12. Include them in your meals to boost your intake of this essential nutrient.

# Eggs
Eggs, particularly the yolk, are a valuable source of vitamin B12. Incorporate eggs into your diet by enjoying them boiled, scrambled, or as an ingredient in various dishes.

# Dairy Products
Milk, yogurt, and cheese are excellent sources of vitamin B12, especially for lacto-vegetarians. Choose low-fat or non-fat options for a healthier choice.

# Fortified Foods
Certain plant-based milk alternatives, breakfast cereals, and nutritional yeast are fortified with vitamin B12. Check the labels to ensure adequate vitamin B12 content if you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet.

# Fortified Meat Substitutes
Some meat substitutes like veggie burgers or soy-based products are fortified with vitamin B12. Look for products specifically labeled as containing added vitamin B12 to meet your nutritional needs.





