- Home›
- Healthy Living›
- World No Tobacco Day : Smoking - A Significant Risk Factor For Bladder Cancer
World No Tobacco Day : Smoking - A Significant Risk Factor For Bladder Cancer
By: Priyanka Maheshwari Wed, 31 May 2023 08:39:08
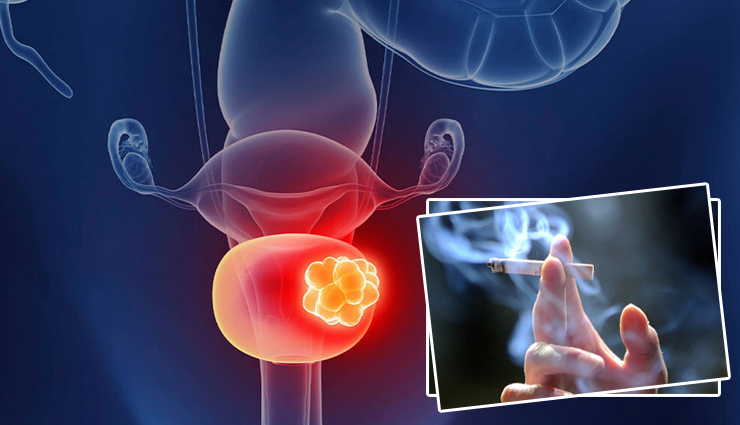
Bladder cancer is a form of cancer that affects the cells of the bladder, which is the organ that stores pee. It is a significant condition with major consequences for a person's health and quality of life. Several risk factors contribute to the development of bladder cancer, and smoking is a substantial and preventable risk factor.
Every year on May 31st, the world commemorates World No Tobacco Day. The World Health Organisation (WHO) organises it to promote awareness about the detrimental consequences of tobacco use and to advocate for effective measures to reduce tobacco usage globally. The campaign emphasises the hazards of tobacco use, promotes cigarette cessation, and encourages governments to undertake tobacco control measures.
In this post, on World No Tobacco Day we will look at the significant link between smoking and bladder cancer, as well as the processes involved and the necessity of quitting smoking for lowering the risk.

The Link Between Smoking and Bladder Cancer:
Extensive research has demonstrated a strong correlation between smoking and bladder cancer. In fact, smoking is considered the most significant risk factor for this disease, accounting for approximately half of all bladder cancer cases. Smokers are at least three times more likely to develop bladder cancer compared to non-smokers, and the risk increases with the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the duration of smoking.

Mechanisms Involved:
Cigarette smoke includes several carcinogens, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and aromatic amines. These compounds enter the circulation after being breathed and are filtered by the kidneys before reaching the bladder. Toxic substances in cigarette smoke can then harm the cells lining the bladder, resulting in malignant growths.
Additionally, the by-products of cigarette smoke, such as reactive oxygen species, can cause oxidative stress, DNA damage, and inflammation within the bladder. These molecular changes can disrupt normal cellular functions and promote the growth of abnormal cells, which can progress into bladder cancer over time.

The Importance of Smoking Cessation:
While the link between smoking and bladder cancer is concerning, there is some good news. Even among long-term smokers, quitting smoking reduces the chance of developing bladder cancer considerably. Individuals who stop smoking can have a progressive decrease in their risk over time, and after many years of sobriety, their risk can approach that of a nonsmoker.
Smoking cessation not only benefits individuals who have never been diagnosed with bladder cancer but also those who have already been treated for the disease. Continued smoking after bladder cancer treatment increases the risk of recurrence, as well as the risk of developing other smoking-related health conditions.

Taking Action:
To reduce the risk of bladder cancer associated with smoking, it is crucial to encourage individuals to quit smoking or never start in the first place. Governments, healthcare professionals, and communities should work together to implement comprehensive tobacco control measures, including public awareness campaigns, smoking cessation programs, and increased access to resources for quitting smoking.
Furthermore, it is critical to assist persons in their efforts to quit smoking. Nicotine replacement treatment, medicines, counselling, and behavioural support can all help people quit smoking. We can empower individuals to take charge of their health and decrease the burden of bladder cancer by giving these materials and fostering a supportive atmosphere.





